An Extra Drug or More of the Same for Uncontrolled Hypertension?
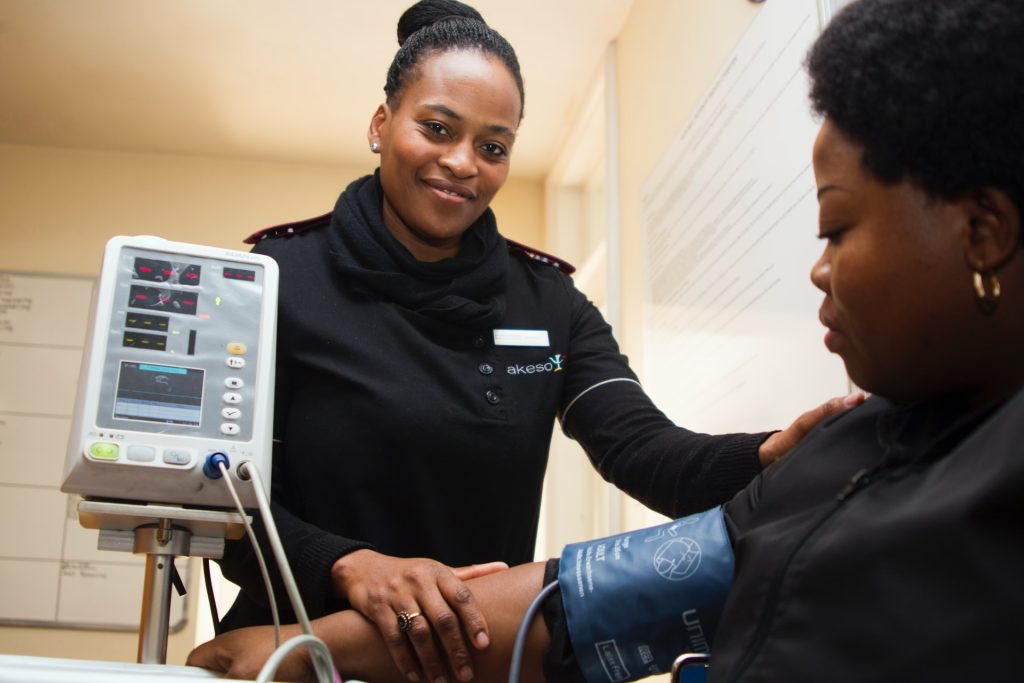
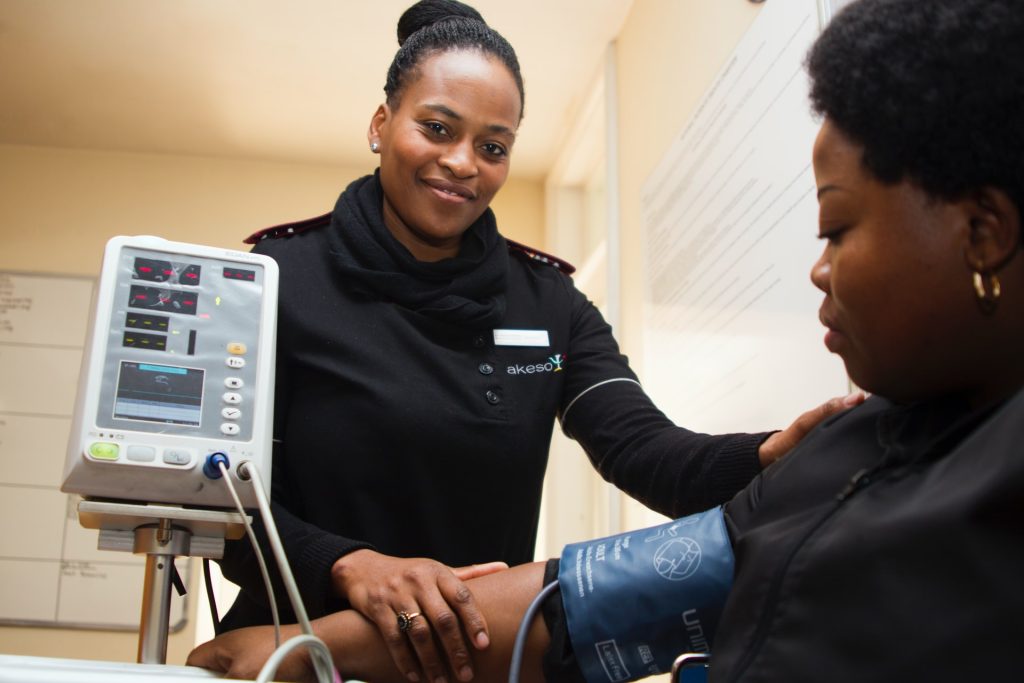
A new study may help people with uncontrolled hypertension and their doctors decide whether to increase the dose of one of their existing drugs, or add a new one, to bring down their blood pressure.
Reviewing data from veterans over age 65 receiving treatment over two years, researchers found that patients have a better chance of adhering to their medication regimen if their doctor maximises the dosage of one of the drugs they’re already taking. While both strategies decrease blood pressure, they found adding a new medication has a very slim advantage over increasing the dose of an existing medication, despite some of the patients being unable to stay on the new medication.
In the end, the researchers say, the new findings could add to discussions between physicians and patients whose blood pressure remains elevated despite starting medication treatment.
The findings, reported in the Annals of Internal Medicine, focus on patients whose initial systolic blood pressure was above 130mmHg.
By looking back at VA and Medicare data, the researchers were able to see patterns in treatment and blood pressure readings over time, in a kind of natural experiment. All the patients were taking at least one blood pressure medication at less than the maximum dose and had a treatment intensification at the start of the study period, indicating that their physicians thought they needed more intense treatment.
Intensifying treatment must be carefully considered, as there are many concerns — whether a drug interaction if a new drug is added, or an electrolyte imbalance with high doses, or fainting and falling if a person’s pressure gets too low .
This is the first time the two approaches have been compared, said first author Dr Carole E. Aubert.
“There’s increasing guidance on approaches to starting treatment in older adults, but less on to the next steps to intensify treatment, especially in an older and medically complex population that isn’t usually included in clinical trials of blood pressure medication,” she said. “How can we increase medications safely in a population already taking many medications for hypertension and other conditions.”
“Treatment guidelines do suggest starting treatment with multiple medications, and clinicians are comfortable with an approach of ‘starting low and going slow’ in older patients,” said senior author Dr Lillian Min. “But these results show that in older patients, we have further opportunity to tailor choices in intensifying drug therapy for hypertension, depending on the individual patient’s characteristics.”
She continued, “Is the patient more likely to stick to a simpler regimen? Then increase an existing medication. Or is the blood pressure very high and the clinician is more concerned about reducing it? Then consider starting a new medication now.”
For older adults already on various medications, overcomplicating it with another pill may be excessive. The risks of polypharmacy are already well known, Dr Min said.
Source: University of Michigan